
Global Developmental Delay (GDD)
Global Developmental Delay (GDD) is a disorder that affects a child’s progress in multiple areas of development. It is characterized by a significant delay in achieving developmental milestones, such as motor skills, speech and language, cognitive abilities, and social and emotional skills. GDD is not a specific diagnosis, but rather a term used to describe a delay in overall development.
The causes of GDD can vary and may include genetic factors, birth complications, environmental factors, or a combination of these. The symptoms of GDD can manifest differently in each child, but common signs include delayed motor skills, difficulty with speech and language, limited cognitive abilities, and challenges with social interactions. These delays can be identified through developmental screenings and assessments.
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for children with GDD. Treatment options may include physical therapy to improve motor skills, speech therapy to enhance communication abilities, occupational therapy to develop daily living skills, and behavioral therapy to address social and emotional challenges. Individualized treatment plans are designed to target the specific needs of each child and help them reach their full potential.
In conclusion, understanding global developmental delay is essential for parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals in order to provide appropriate support and resources for children affected by this disorder. By recognizing the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, we can work towards ensuring that every child with GDD receives the necessary interventions to promote their development and overall well-being.
Understanding Global Developmental Delay (GDD)
Global Developmental Delay (GDD) is a disorder that affects a child’s overall development, including their cognitive, physical, and social skills. It is characterized by a significant delay in achieving developmental milestones compared to other children of the same age.
There can be various causes for GDD, including genetic factors, prenatal or birth complications, or environmental factors. It is important to seek early intervention and diagnosis to determine the underlying cause and provide appropriate therapy and support for the child.
The symptoms of GDD can vary depending on the individual child, but they often include delays in language and speech development, fine and gross motor skills, social interaction, and cognitive abilities. These delays can have a significant impact on the child’s daily life and may require specialized therapy and educational support.
Diagnosing GDD involves a comprehensive evaluation of the child’s development, including physical examinations, developmental assessments, and medical tests. This process helps to identify the specific areas of delay and determine the most effective treatment plan.
Therapy for GDD typically involves a multidisciplinary approach, including speech therapy, occupational therapy, and physical therapy. These interventions aim to improve the child’s communication skills, motor abilities, and overall development. Additionally, early intervention programs and specialized education can provide additional support for children with GDD.
In conclusion, understanding Global Developmental Delay (GDD) is crucial for parents, caregivers, and healthcare professionals to provide appropriate interventions and support for children with this disorder. Early diagnosis and therapy can significantly improve the child’s developmental outcomes and quality of life.
Causes of Global Developmental Delay
Global developmental delay (GDD) can have various causes that affect a child’s progress in different areas of development. It is important to understand these causes in order to provide appropriate intervention and therapy for the child.
One of the main causes of global developmental delay is genetic disorders. Certain genetic abnormalities or mutations can disrupt the normal development of the child, leading to delays in cognitive, motor, and social skills. Examples of genetic disorders that can cause GDD include Down syndrome, fragile X syndrome, and Rett syndrome.
Another common cause of global developmental delay is prenatal factors. Exposure to certain substances during pregnancy, such as alcohol, drugs, or infections, can have a negative impact on the development of the fetus. Premature birth and low birth weight are also risk factors for GDD.
Environmental factors can also contribute to global developmental delay. Lack of stimulation, neglect, or abuse can hinder a child’s development. Additionally, living in a disadvantaged socio-economic environment can limit access to resources and opportunities for early intervention and therapy.
Medical conditions and health issues can also play a role in global developmental delay. Brain injuries, seizures, and metabolic disorders can affect the child’s neurological development and result in delays. Chronic illnesses or conditions that affect the child’s overall health can also impact their development.
In some cases, the cause of global developmental delay may not be identified. This is known as idiopathic GDD. It is important for healthcare professionals to conduct a thorough evaluation and assessment to determine the underlying causes and provide appropriate support and treatment for the child.
Symptoms of Global Developmental Delay
Global Developmental Delay (GDD) is a disorder that affects a child’s overall development. It is characterized by significant delays in various areas of development, including motor skills, language and communication, cognitive abilities, and social and emotional skills.
One of the key symptoms of GDD is a delay in reaching developmental milestones. Children with GDD may take longer than expected to sit up, crawl, walk, talk, or engage in age-appropriate play. They may also have difficulty with basic self-care tasks, such as feeding themselves or dressing.
In addition to delays in motor and language skills, children with GDD may also exhibit other symptoms. These can include difficulties with attention and concentration, problems with memory and problem-solving, and challenges with social interactions. They may have trouble following instructions, understanding and using language, and interacting with peers.
Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial for children with GDD. Therapy and intervention programs, such as physical therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy, can help improve the child’s development and overall functioning. With appropriate intervention, children with GDD can make progress and reach their full potential.
Diagnosis of Global Developmental Delay
Diagnosing global developmental delay (GDD) can be a complex process that requires a comprehensive evaluation of the child’s development and functioning. The diagnosis is typically made by a team of healthcare professionals, including pediatricians, neurologists, psychologists, and other specialists.
During the diagnostic process, the child’s developmental milestones are assessed, including motor skills, speech and language development, cognitive abilities, and social interactions. The healthcare team will also conduct a thorough physical examination and may order additional tests, such as genetic testing or brain imaging, to rule out other possible causes of the delay.
It is important to note that GDD is not a specific disorder, but rather a descriptive term used to categorize children who have significant delays in multiple areas of development. The underlying cause of GDD can vary widely, including genetic disorders, brain abnormalities, environmental factors, or a combination of factors.
Early intervention is crucial for children with GDD, as it can help improve their developmental outcomes. Once a diagnosis of GDD is made, a tailored intervention plan is developed to address the specific needs of the child. This may include various therapies, such as speech therapy, occupational therapy, and physical therapy, as well as educational interventions.
In conclusion, the diagnosis of global developmental delay involves a comprehensive evaluation of the child’s development and functioning. It is important to identify the underlying cause of the delay and develop an individualized intervention plan to support the child’s development and improve their outcomes.
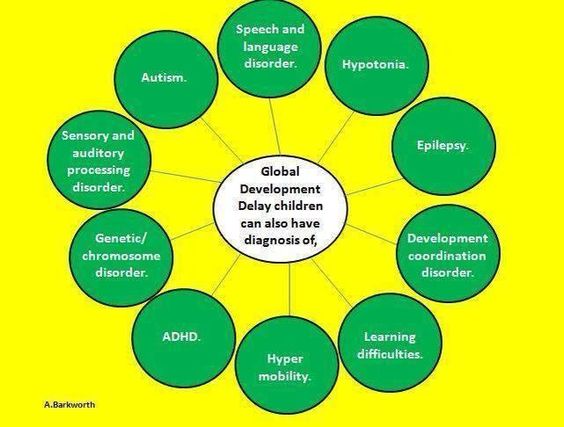
Types of Global Developmental Delay
Global developmental delay (GDD) is a disorder that affects a child’s overall development in multiple areas, including cognitive, social, and physical development. There are several types of GDD, each with its own distinct characteristics and patterns of delay.
1. Intellectual developmental delay: This type of GDD is characterized by significant delays in cognitive development, including language skills, problem-solving abilities, and memory. Children with intellectual developmental delay may have difficulties with learning and may require specialized educational interventions and therapies.
2. Motor developmental delay: Motor developmental delay refers to delays in the development of gross motor skills, such as crawling, walking, and running, as well as fine motor skills, such as grasping objects and using utensils. Physical therapy and occupational therapy are often used to help children with motor developmental delay improve their motor skills.
3. Speech and language developmental delay: This type of GDD involves delays in the development of speech and language skills. Children with speech and language developmental delay may have difficulties with articulation, vocabulary, and understanding and expressing language. Speech therapy is typically recommended to help improve communication skills.
4. Social and emotional developmental delay: Social and emotional developmental delay refers to delays in the development of social and emotional skills, such as interacting with others, understanding and expressing emotions, and forming relationships. Early intervention programs and therapies, such as play therapy and social skills training, can help children with social and emotional developmental delay improve their social and emotional functioning.
5. Adaptive developmental delay: Adaptive developmental delay involves delays in the development of adaptive skills, which are necessary for daily living and functioning independently. These skills include self-care skills, such as dressing and feeding oneself, as well as skills related to personal hygiene and safety. Occupational therapy and other interventions can help children with adaptive developmental delay acquire and improve these skills.
It is important to note that these types of GDD are not mutually exclusive, and many children may experience delays in multiple areas of development. A comprehensive evaluation and diagnosis by a healthcare professional is necessary to determine the specific types of GDD a child may have and to develop an individualized treatment plan.
Early Intervention for Global Developmental Delay
Early intervention plays a crucial role in addressing global developmental delay in children. Global developmental delay is a disorder that affects a child’s progress in multiple areas of development, including cognitive, physical, and social skills. It is important to diagnose and intervene as early as possible to optimize the child’s potential for improvement.
When a child is diagnosed with global developmental delay, it is essential to implement appropriate interventions to address their specific needs. These interventions can include various therapies such as speech therapy, occupational therapy, and physical therapy. Each therapy focuses on different aspects of the child’s development, such as communication, fine motor skills, and gross motor skills.
Early intervention programs for global developmental delay are typically tailored to the individual child’s needs. These programs involve a multidisciplinary approach, with a team of professionals working together to provide comprehensive support. The team may include pediatricians, psychologists, therapists, and educators, who collaborate to create a personalized intervention plan.
Interventions for global developmental delay aim to promote the child’s overall development and help them reach their full potential. The therapies provided in early intervention programs are designed to target specific areas of delay and encourage progress. The interventions may involve structured activities, play-based approaches, and specialized techniques to support the child’s learning and development.
Early intervention for global developmental delay is crucial because it can significantly improve outcomes for children. Research has shown that early intervention can lead to better long-term outcomes, including improved cognitive abilities, language skills, and social interactions. By identifying and addressing developmental delays early on, children have a greater chance of catching up to their peers and achieving their developmental milestones.
Speech and Language Therapy for Global Developmental Delay
Speech and language therapy is an essential intervention for children with global developmental delay (GDD). GDD is a disorder that affects a child’s overall development, including their speech and language skills. It is typically diagnosed when a child’s development is significantly delayed in multiple areas, such as motor skills, cognitive abilities, and communication.
The goal of speech and language therapy for children with GDD is to improve their communication skills and help them reach their full potential. The therapy focuses on developing a child’s speech and language abilities through targeted interventions and techniques.
During therapy sessions, a speech and language therapist will assess the child’s current level of speech and language development and create a personalized treatment plan. This plan may include activities to improve language comprehension, expressive language skills, articulation, and social communication.
Therapists often use a variety of techniques to engage the child and facilitate their speech and language development. These may include play-based activities, interactive games, storytelling, and the use of visual aids. The therapist may also work closely with the child’s parents and caregivers to provide guidance and support for practicing speech and language skills at home.
Speech and language therapy for children with GDD is a long-term process that requires consistency and patience. The therapy sessions are typically conducted on a regular basis, and progress is monitored closely. The ultimate goal is to help the child overcome their communication difficulties and improve their overall development.
In conclusion, speech and language therapy plays a crucial role in the intervention and treatment of global developmental delay. It focuses on improving a child’s speech and language skills, helping them communicate effectively, and enhancing their overall development.
Physical Therapy for Global Developmental Delay
Physical therapy plays a crucial role in the diagnosis and treatment of global developmental delay (GDD). GDD is a disorder that affects a child’s overall development and progress in various areas, including motor skills, speech and language, and cognitive abilities. Physical therapy focuses on improving the child’s physical development and motor skills.
During physical therapy sessions, a trained therapist works with the child to assess their current physical abilities and identify areas of delay or weakness. The therapist then designs a personalized intervention plan to address these specific areas and promote overall development.
The therapy sessions may include a variety of exercises and activities tailored to the child’s needs. These may involve strengthening exercises, balance and coordination activities, and gross motor skill development. The therapist may also incorporate play-based interventions to make the sessions engaging and enjoyable for the child.
Physical therapy for GDD aims to improve the child’s strength, flexibility, and coordination, which are essential for their overall physical development. The therapy sessions not only help the child acquire new skills but also enhance their confidence and independence.
Regular physical therapy sessions, combined with other interventions such as speech therapy and occupational therapy, can significantly improve the outcomes for children with global developmental delay. It is important for parents and caregivers to work closely with the therapy team and follow the recommended treatment plan to ensure the best possible results for the child.
Occupational Therapy for Global Developmental Delay
Occupational therapy is an essential component of the overall treatment plan for children with global developmental delay (GDD). GDD is a disorder that affects a child’s progress and development in multiple areas, including motor skills, cognitive abilities, speech and language, and social and emotional skills.
Occupational therapists play a crucial role in the diagnosis and intervention of GDD. They work closely with the child and their family to assess their specific needs and develop a personalized therapy plan. This plan may include various activities and exercises aimed at improving the child’s motor skills, sensory processing abilities, and overall functional independence.
One of the main goals of occupational therapy for GDD is to address the delays and difficulties that the child may be experiencing in their daily activities. This can include tasks such as self-care activities (e.g., dressing, feeding), play skills, school-related tasks, and social interactions. The therapist may use a combination of techniques, such as sensory integration therapy, fine motor skills training, and cognitive exercises, to help the child overcome these challenges.
Occupational therapy for GDD is typically provided in a structured and supportive environment, such as a clinic or school setting. The therapist may work one-on-one with the child or in a group setting, depending on their specific needs. The therapy sessions may involve a variety of activities, such as playing with toys, using specialized equipment, engaging in sensory play, and practicing daily life skills.
Overall, occupational therapy can have a significant impact on a child with global developmental delay. It can help improve their motor skills, enhance their cognitive abilities, and promote their overall development and independence. With early intervention and consistent therapy, children with GDD can make progress and achieve their full potential.
Behavioral Therapy for Global Developmental Delay
Behavioral therapy is an essential intervention for children with global developmental delay (GDD). GDD is a disorder that affects a child’s overall development, including their cognitive, motor, and social skills. It is typically diagnosed when a child’s progress in these areas is significantly delayed compared to their peers.
Behavioral therapy focuses on addressing the specific developmental needs of the child and helping them acquire the skills necessary for their overall development. It involves a structured and individualized approach that targets specific areas of development, such as language and communication, social skills, and self-help skills.
One of the key goals of behavioral therapy for GDD is to improve the child’s ability to function independently and interact effectively with others. This may involve teaching them appropriate social behaviors, such as taking turns, sharing, and following instructions. It may also involve helping them develop self-help skills, such as dressing, feeding, and toileting.
Behavioral therapy for GDD typically involves a combination of techniques, including applied behavior analysis (ABA), which focuses on breaking down skills into smaller, manageable steps and using positive reinforcement to encourage desired behaviors. Other techniques may include play therapy, speech therapy, and occupational therapy, depending on the specific needs of the child.
It is important to note that behavioral therapy for GDD is not a one-size-fits-all approach. Each child’s therapy plan should be tailored to their specific needs and strengths. Regular assessment and monitoring are essential to track the child’s progress and make any necessary adjustments to the therapy plan.
In conclusion, behavioral therapy is a crucial intervention for children with global developmental delay. It aims to address the specific developmental needs of the child and help them acquire the skills necessary for their overall development. Through a structured and individualized approach, behavioral therapy can significantly improve a child’s ability to function independently and interact effectively with others.
Educational Support for Global Developmental Delay
Children with global developmental delay (GDD) require specialized educational support to help them overcome their challenges and make progress in their development. Educational intervention plays a crucial role in addressing the specific needs of these children and helping them reach their full potential.
Diagnosis of global developmental delay can be a complex process, as it involves assessing a child’s overall development in multiple areas, including cognitive, motor, and social-emotional skills. Once a child has been diagnosed with GDD, an individualized education plan (IEP) is often created to outline specific goals and strategies for their educational support.
Therapy and intervention services are key components of educational support for children with global developmental delay. These services can include speech therapy, occupational therapy, and physical therapy, among others. These therapies aim to improve the child’s communication skills, motor abilities, and overall development.
Teachers and educators play a crucial role in providing educational support to children with GDD. They need to be trained in understanding the specific needs and challenges of these children and implementing appropriate strategies to support their learning. This may involve using visual aids, simplified instructions, and providing additional support and guidance.
It is important to note that educational support for global developmental delay should be individualized and tailored to each child’s unique needs. The progress of the child should be regularly monitored, and adjustments should be made to the educational plan as necessary. With the right support and intervention, children with GDD can make significant progress in their development and reach their full potential.
Medical Treatments for Global Developmental Delay
When a child is diagnosed with global developmental delay (GDD), it is important to start medical interventions as soon as possible to help the child make progress in their development. There are various medical treatments available that can help improve the child’s overall development and address specific areas of delay.
One common medical intervention for GDD is therapy. This can include occupational therapy, speech therapy, and physical therapy. These therapies are designed to target specific areas of delay, such as fine motor skills, communication skills, and gross motor skills. Through regular therapy sessions, a child with GDD can improve their abilities and reach developmental milestones.
Another medical treatment for GDD is medication. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to address underlying medical conditions that are contributing to the developmental delay. For example, if a child has seizures that are causing delays in their development, anticonvulsant medication may be prescribed to help control the seizures and improve overall functioning.
In addition to therapy and medication, early intervention programs can also play a crucial role in treating GDD. These programs provide comprehensive support and services to children with developmental delays, including educational interventions, social-emotional support, and parent training. Early intervention programs are designed to promote optimal development in children with GDD and help them reach their full potential.
It is important to note that medical treatments for GDD are not a one-size-fits-all approach. Each child with GDD is unique, and their treatment plan should be tailored to their specific needs and abilities. A multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals, including doctors, therapists, and educators, will work together to develop an individualized treatment plan for each child with GDD, taking into account their strengths, challenges, and goals.
Supporting a Child with Global Developmental Delay
When a child is diagnosed with global developmental delay (GDD), it is important to provide them with the necessary support to help them overcome their challenges and reach their full potential. Developmental delay refers to a disorder in which a child is significantly behind their peers in achieving developmental milestones in multiple areas, such as cognitive, motor, and social skills.
Therapy plays a crucial role in supporting a child with global developmental delay. Early intervention is key, as it can help address the specific areas of delay and promote development. A combination of occupational therapy, speech therapy, and physical therapy may be recommended based on the child’s individual needs. These therapies aim to improve the child’s motor skills, communication abilities, and overall cognitive functioning.
It is important to create a nurturing and stimulating environment for the child to encourage their progress. Providing a consistent routine and structure can help the child feel secure and supported. Engaging in activities that promote development, such as playing with age-appropriate toys, reading books, and engaging in interactive games, can also aid in their overall growth.
Support from family, friends, and educators is essential in helping a child with global developmental delay. It is important to communicate openly and regularly with the child’s healthcare team and therapists to ensure a coordinated approach to their care. These professionals can provide guidance on strategies and techniques to support the child’s development and address any specific challenges they may be facing.
Every child with global developmental delay is unique, and their progress may vary. It is important to celebrate and acknowledge their achievements, no matter how small they may seem. Patience, understanding, and unconditional love are crucial in supporting a child with GDD on their developmental journey.
Outlook for Children with Global Developmental Delay
Children diagnosed with Global Developmental Delay (GDD) face challenges in their overall development and may experience delays in reaching milestones compared to their peers.
The outlook for children with GDD varies depending on the underlying causes of the disorder and the individual child’s progress. Early diagnosis and intervention are crucial in providing appropriate support and therapy to help children with GDD reach their full potential.
With proper therapy and support, many children with GDD can make significant progress in their development. Occupational therapy, speech therapy, and physical therapy are often recommended to address specific areas of delay and help children improve their skills.
It is important to note that each child with GDD is unique, and their progress will vary. Some children may catch up to their peers with time and intervention, while others may continue to experience delays throughout their lives. It is essential to focus on each child’s individual strengths and provide tailored support to optimize their development.
Parents and caregivers play a crucial role in the outlook for children with GDD. Providing a nurturing and stimulating environment, engaging in early intervention programs, and advocating for the child’s needs can greatly contribute to their overall development.
While the journey may present challenges, it is important to remain optimistic and celebrate every achievement, no matter how small. By understanding and addressing the unique needs of children with GDD, we can help them thrive and reach their full potential in life.
Question-answer:
What is Global Developmental Delay (GDD)?
Global Developmental Delay (GDD) refers to a condition in which a child experiences delays in multiple areas of development, including motor skills, speech and language, cognitive abilities, and social and emotional skills. It is typically diagnosed before the age of 5 and can have various causes.
What are the common causes of Global Developmental Delay?
There are several potential causes of Global Developmental Delay, including genetic disorders, prenatal factors such as exposure to toxins or infections, complications during birth, medical conditions such as hearing or vision impairments, and environmental factors such as neglect or abuse.
How is Global Developmental Delay diagnosed?
Diagnosing Global Developmental Delay involves a comprehensive evaluation of a child’s developmental milestones and abilities. This may include physical examinations, developmental assessments, medical history review, genetic testing, and other diagnostic tests to rule out any underlying conditions that may be causing the delay.
What are the symptoms of Global Developmental Delay?
Symptoms of Global Developmental Delay can vary depending on the specific areas of development that are affected. Some common signs may include delays in reaching motor milestones (such as sitting up, crawling, or walking), difficulties with speech and language development, cognitive delays, social and emotional challenges, and behavior problems.
Is there any treatment available for Global Developmental Delay?
Treatment for Global Developmental Delay typically involves a multidisciplinary approach that may include therapies such as physical therapy, occupational therapy, speech therapy, and behavioral interventions. The specific treatment plan will depend on the individual needs of the child and may also involve medications or assistive devices.