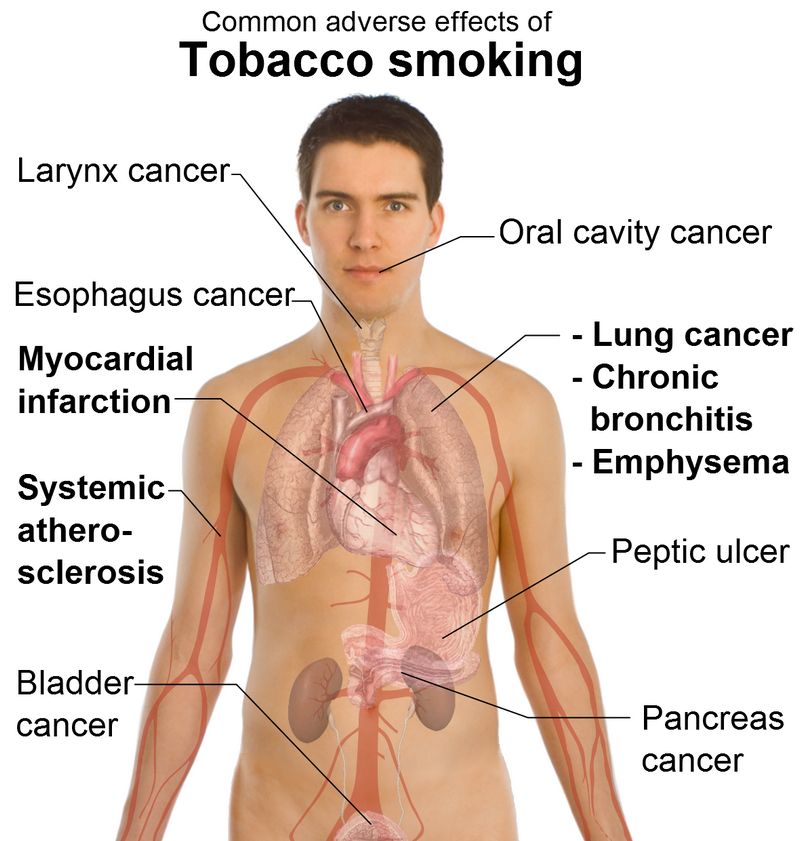
Side Effects of Tobacco
Tobacco use, particularly smoking, is a leading cause of preventable deaths worldwide. One of the main reasons for this is the presence of nicotine in tobacco products. Nicotine is a highly addictive substance that affects the brain and central nervous system, leading to dependence and addiction.
Smoking tobacco has been linked to a wide range of health problems, including heart disease. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the lining of the arteries, leading to a buildup of plaque and increasing the risk of heart attacks and strokes.
In addition to heart disease, smoking tobacco is also a major cause of various types of cancer. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the DNA in cells, leading to the development of cancerous cells in the lungs, throat, mouth, and other parts of the body.
Furthermore, smoking tobacco is a major risk factor for lung disease. The inhalation of tobacco smoke can cause inflammation and damage to the lungs, leading to conditions such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema. It can also worsen existing respiratory conditions such as asthma.
It is important to recognize the harmful side effects of tobacco use and take steps to quit smoking or avoid tobacco products altogether. The addictive nature of nicotine can make quitting a challenge, but there are resources and support available to help individuals overcome their addiction and improve their overall health.
Tobacco Use and Its Consequences
Smoking tobacco has numerous harmful effects on the human body. One of the most serious consequences of tobacco use is an increased risk of stroke. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the blood vessels and increase the chances of a blood clot forming in the brain, leading to a stroke.
Another major consequence of tobacco use is the increased risk of developing various types of cancer. Smoking tobacco exposes the body to carcinogens, which can cause mutations in the DNA and lead to the development of cancer cells. Lung cancer is the most well-known cancer associated with smoking, but tobacco use can also increase the risk of other types of cancer, such as mouth, throat, and pancreatic cancer.
Death is another consequence of tobacco use. Smoking is the leading cause of preventable deaths worldwide. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke can cause serious health problems, such as heart disease and lung disease, which can ultimately lead to death.
Nicotine, the addictive substance in tobacco, has its own set of consequences. Nicotine can increase heart rate and blood pressure, putting additional strain on the heart. This can lead to an increased risk of heart disease, heart attacks, and other cardiovascular problems.
In addition to the risks of stroke and cancer, smoking tobacco can also cause serious damage to the lungs. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can irritate the airways and lead to the development of chronic respiratory conditions, such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema. These conditions can make it difficult to breathe and significantly impact quality of life.
Overall, tobacco use has numerous harmful consequences for the human body. From an increased risk of stroke and cancer to the potential for death and damage to the heart and lungs, the negative effects of smoking are extensive. It is important to understand these consequences and make informed choices about tobacco use to protect our health.
The Health Risks of Smoking
Smoking poses a significant risk to the health of individuals. It has been proven to be a leading cause of heart disease, lung cancer, and other serious health conditions. The harmful effects of smoking are primarily attributed to the presence of nicotine, a highly addictive substance found in tobacco products.
One of the most well-known health risks associated with smoking is an increased risk of heart disease. Smoking damages the arteries and causes them to narrow, which can lead to heart attacks and other cardiovascular problems. The chemicals in tobacco smoke also contribute to the formation of blood clots, further increasing the risk of heart-related issues.
In addition to heart disease, smoking is a major contributor to lung cancer. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke, including carcinogens, can cause abnormal cell growth in the lungs, leading to the development of cancerous tumors. Lung cancer is one of the leading causes of cancer-related deaths worldwide, and smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer.
Smoking also increases the risk of stroke, a potentially life-threatening condition. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the blood vessels in the brain, leading to reduced blood flow and an increased risk of blood clots. This can result in a stroke, which can cause permanent damage to the brain or even death.
Furthermore, smoking is linked to an increased risk of various other diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), emphysema, and respiratory infections. These conditions can cause significant breathing difficulties and reduce the overall quality of life for individuals who smoke.
It is important to note that the health risks associated with smoking are not limited to the individuals who smoke. Secondhand smoke, which is the smoke exhaled by smokers or released from burning tobacco products, can also be harmful to others. Secondhand smoke has been linked to an increased risk of respiratory infections, asthma, and even sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS) in infants.
In conclusion, smoking poses serious health risks, including heart disease, lung cancer, stroke, and various other diseases. Quitting smoking is essential for improving overall health and reducing the risk of these life-threatening conditions.
Smoking and Lung Cancer
Smoking is the leading cause of lung cancer. It is estimated that about 85% of lung cancer cases are directly related to smoking. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke, such as nicotine and tar, can damage the cells in the lungs and lead to the development of cancerous tumors.
Lung cancer is a serious disease that can be life-threatening. It is characterized by the uncontrolled growth of abnormal cells in the lung tissues. These cancer cells can spread to other parts of the body, including the lymph nodes, liver, bones, and brain, causing further complications and reducing the chances of survival.
Smoking not only increases the risk of developing lung cancer, but it also increases the risk of other types of cancer, such as mouth, throat, esophageal, bladder, kidney, and pancreatic cancer. Additionally, smoking can also lead to heart disease, stroke, and other respiratory diseases.
Nicotine, the addictive substance in tobacco, is what makes smoking so hard to quit. It stimulates the release of dopamine in the brain, creating a pleasurable sensation and reinforcing the habit of smoking. This addiction can make it extremely difficult for smokers to quit, even when they are aware of the harmful effects.
To protect your health and reduce the risk of lung cancer, it is important to quit smoking or never start in the first place. If you are a smoker, seek support from healthcare professionals and consider nicotine replacement therapies or other cessation methods to help you quit. Remember, it is never too late to quit smoking and improve your health.
Smoking and Cardiovascular Diseases
Smoking is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, which include conditions such as heart disease, stroke, and peripheral artery disease. The harmful effects of smoking on the cardiovascular system are primarily due to the nicotine and other chemicals present in tobacco.
Nicotine, the addictive substance in tobacco, increases heart rate and blood pressure, causing the heart to work harder. This puts a strain on the heart and can lead to the development of heart disease. Smoking also promotes the formation of blood clots, which can block the blood vessels and result in a heart attack or stroke.
Long-term smoking can cause damage to the lining of the blood vessels, making them narrower and less flexible. This condition, known as atherosclerosis, restricts blood flow to the heart and other organs, increasing the risk of heart disease and other cardiovascular problems.
In addition to heart disease and stroke, smoking is also linked to an increased risk of peripheral artery disease, a condition in which the blood vessels in the arms and legs become narrowed or blocked. This can lead to pain, numbness, and difficulty walking.
It is important to note that smoking not only increases the risk of developing cardiovascular diseases, but also worsens the outcomes for those who already have these conditions. Smokers with heart disease are more likely to experience a heart attack or sudden cardiac death compared to non-smokers with the same condition.
Quitting smoking is the best way to reduce the risk of cardiovascular diseases and improve overall health. The sooner one quits, the greater the benefits. It is never too late to quit smoking and start on the path to a healthier heart and a longer life.
Smoking and Respiratory Diseases
Smoking is a dangerous habit that affects not only the smoker but also those around them. One of the most serious consequences of smoking is the development of respiratory diseases.
Smoking is an addiction that is fueled by the presence of nicotine in tobacco products. When a person smokes, the nicotine enters their bloodstream and reaches the brain within seconds. This addictive substance causes a release of dopamine, which creates a pleasurable sensation. However, this addiction comes at a high cost to the respiratory system.
One of the most well-known respiratory diseases caused by smoking is lung cancer. The toxic chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the cells in the lungs, leading to the growth of cancerous tumors. Lung cancer is a deadly disease that can result in a slow and painful death.
In addition to lung cancer, smoking also increases the risk of developing other respiratory diseases such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). COPD is a progressive disease that causes difficulty breathing and is often characterized by chronic coughing and wheezing. It can significantly reduce a person’s quality of life and can even lead to disability and death.
Smoking is also a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, including stroke and heart disease. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the blood vessels and increase the risk of blood clots, which can lead to a stroke or heart attack. These conditions can have severe consequences and can result in disability or death.
Overall, smoking has devastating effects on the respiratory system and increases the risk of developing various respiratory diseases, including lung cancer and COPD. It is also a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases. Quitting smoking is the best way to prevent these harmful consequences and improve overall health.
Secondhand Smoke and Its Dangers
Secondhand smoke refers to the smoke that is exhaled by smokers or emitted from the burning end of a cigarette. It contains more than 7,000 chemicals, including at least 70 that can cause cancer. Exposure to secondhand smoke can have serious health consequences.
One of the dangers of secondhand smoke is its link to respiratory problems. Breathing in secondhand smoke can irritate the airways and trigger asthma attacks in individuals with asthma. It can also worsen symptoms in people with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). In addition, exposure to secondhand smoke increases the risk of respiratory infections, such as bronchitis and pneumonia.
Secondhand smoke is also associated with an increased risk of heart disease. The chemicals in the smoke can damage the lining of the blood vessels, making them more prone to the formation of blood clots. This can lead to a heart attack or stroke. Non-smokers who are regularly exposed to secondhand smoke have a 25-30% higher risk of developing heart disease compared to those who are not exposed.
Furthermore, exposure to secondhand smoke can have harmful effects on children. Children who are exposed to secondhand smoke are at a higher risk of developing respiratory infections, asthma, ear infections, and sudden infant death syndrome (SIDS). They may also experience impaired lung function and may have a higher likelihood of becoming smokers themselves later in life.
It is important to note that there is no safe level of exposure to secondhand smoke. Even brief exposure can be harmful. To protect yourself and your loved ones from the dangers of secondhand smoke, it is essential to create smoke-free environments and avoid places where smoking is allowed.
Smoking and Oral Health
Smoking is not only harmful to the heart and lungs, but it also has detrimental effects on oral health. The harmful chemicals present in tobacco products can lead to a variety of oral health problems.
One of the most common oral health issues caused by smoking is gum disease. Smoking weakens the immune system, making it harder for the body to fight off infection. This can result in inflammation and infection of the gums, leading to gum disease. In severe cases, gum disease can cause tooth loss.
Another oral health problem associated with smoking is oral cancer. Tobacco smoke contains numerous carcinogens, including nicotine, which can damage the cells in the mouth and lead to the development of cancerous tumors. Oral cancer can be life-threatening and often requires aggressive treatment, including surgery and radiation therapy.
Smoking also affects the appearance of teeth and can cause tooth discoloration. The tar and nicotine in tobacco products can stain the enamel of the teeth, giving them a yellow or brownish appearance. This can be difficult to reverse and may require professional teeth whitening treatments.
Additionally, smoking can delay the healing process after dental procedures. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can impair blood flow and decrease oxygen levels in the body, which can slow down the healing of oral tissues. This can lead to complications and prolong the recovery time after procedures such as tooth extractions or gum surgery.
In conclusion, smoking has a significant impact on oral health. It increases the risk of gum disease, oral cancer, tooth discoloration, and can delay the healing process. Quitting smoking is crucial for maintaining good oral health and reducing the risk of these harmful side effects.
Smoking and Pregnancy Complications
Smoking during pregnancy can have serious consequences for both the mother and the unborn child. The harmful effects of smoking on the lungs and the cardiovascular system are well-known, but they can be especially detrimental during pregnancy.
One of the most significant complications of smoking during pregnancy is the increased risk of premature birth. Smoking can damage the lungs of the developing fetus and lead to respiratory problems after birth. Babies born prematurely are also at higher risk of other health issues, such as low birth weight and developmental delays.
Smoking during pregnancy can also increase the risk of miscarriage and stillbirth. The toxic chemicals in cigarettes can restrict blood flow to the placenta, depriving the baby of oxygen and nutrients. This can result in serious complications and even death for the unborn child.
In addition to these immediate risks, smoking during pregnancy can have long-term consequences for the child’s health. Babies born to mothers who smoke are more likely to develop respiratory problems, such as asthma and bronchitis, later in life. They are also at higher risk of heart disease, stroke, and certain types of cancer.

Quitting smoking during pregnancy is crucial for the health and well-being of both the mother and the baby. However, quitting can be challenging due to the addictive nature of nicotine. Pregnant women who smoke should seek support from healthcare professionals and explore resources available to help them quit smoking and protect their unborn child from the harmful effects of tobacco use.
Smoking and Infertility
Smoking has been linked to various harmful effects on the body, including heart disease, stroke, and cancer. However, one lesser-known consequence of smoking is its impact on fertility.
Research has shown that smoking can significantly reduce both male and female fertility. In women, smoking can disrupt the delicate hormonal balance necessary for ovulation and can also damage the eggs. This can lead to difficulties in conceiving and an increased risk of miscarriage. In addition, smoking during pregnancy can increase the chances of complications and harm the developing fetus.
For men, smoking can affect sperm quality and quantity. It can lead to a decrease in sperm count, motility, and morphology, making it more difficult to achieve pregnancy. Smoking can also increase the risk of erectile dysfunction, further impacting fertility.
The harmful effects of smoking on fertility can be attributed to the presence of nicotine and other toxic chemicals in cigarettes. Nicotine can cause blood vessels to constrict, reducing blood flow to the reproductive organs and affecting their function. The toxic chemicals in cigarettes can also damage DNA and cause mutations, increasing the risk of infertility and birth defects.
Quitting smoking is essential for those trying to conceive or undergoing fertility treatments. By quitting, individuals can improve their chances of conceiving and reduce the risk of complications during pregnancy. It is important to seek support and resources to overcome the addiction and address any underlying health issues related to smoking.
Smoking and Diabetes
Smoking is a dangerous habit that can lead to severe health consequences, including an increased risk of developing diabetes. Research has shown that smoking can directly contribute to the development of type 2 diabetes, a chronic disease characterized by high blood sugar levels.
Nicotine, the addictive substance found in tobacco products, can affect the body’s ability to use insulin effectively. Insulin is a hormone that helps regulate blood sugar levels, and when its function is impaired, it can lead to the development of diabetes.
In addition to increasing the risk of diabetes, smoking also poses other health risks. It is a known cause of various types of cancer, including lung cancer, and can also lead to heart disease, stroke, and lung disease.
People with diabetes who smoke are at an even higher risk of developing complications. Smoking can worsen the effects of diabetes by causing damage to blood vessels and increasing the risk of cardiovascular problems.
It is important for individuals with diabetes to quit smoking in order to reduce their risk of developing further complications. Quitting smoking can improve blood sugar control and decrease the risk of heart disease and other smoking-related health problems.
If you are a smoker with diabetes, it is important to seek support and resources to help you quit. Talk to your healthcare provider about strategies and medications that can assist with smoking cessation. Remember, quitting smoking is one of the best things you can do for your overall health and well-being.
Smoking and Mental Health
Smoking not only has harmful effects on the lungs and cardiovascular system, but it can also have a negative impact on mental health.
Nicotine, the addictive substance found in cigarettes, can alter brain chemistry and affect mood and behavior. It can increase feelings of anxiety and depression, and make it harder to cope with stress.
Research has shown that smokers are more likely to develop mental health disorders such as anxiety and depression compared to non-smokers. The risk of developing these disorders is even higher for individuals with a history of smoking.
In addition to the direct effects on mental health, smoking can also indirectly contribute to mental health problems. The increased risk of developing lung disease, heart disease, and stroke associated with smoking can lead to a higher risk of disability and premature death. These health issues can have a significant impact on a person’s mental well-being and quality of life.
It is important for individuals with mental health disorders to be aware of the harmful effects of smoking and to seek support in quitting. Quitting smoking can improve mental health outcomes and overall well-being.
Smoking and Aging
Smoking is a harmful habit that has numerous negative effects on the body, including accelerating the aging process. The chemicals found in cigarettes, such as nicotine, can lead to premature aging of the skin and the development of wrinkles. The toxins in tobacco smoke also reduce the amount of collagen and elastin in the skin, which are responsible for its elasticity and firmness.
Furthermore, smoking has been linked to an increased risk of age-related diseases. For example, long-term smokers are more likely to develop lung cancer, as well as other types of cancer such as throat, mouth, and esophageal cancer. The toxins in tobacco smoke can damage the DNA in cells, leading to the uncontrolled growth of cancer cells.
In addition to cancer, smoking also increases the risk of heart disease and stroke. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the lining of the blood vessels, causing them to narrow and harden. This can lead to high blood pressure, blood clots, and ultimately, heart attacks and strokes. Smoking also contributes to the development of atherosclerosis, a condition where plaque builds up in the arteries, further increasing the risk of heart disease.
Smoking has also been linked to other age-related diseases, such as chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) and emphysema. The toxins in tobacco smoke can damage the airways and alveoli in the lungs, leading to difficulty breathing, coughing, and wheezing. Over time, this can progress to more severe respiratory problems and reduced lung function.
In conclusion, smoking not only has immediate harmful effects on the body, but it also accelerates the aging process and increases the risk of age-related diseases. Quitting smoking is the best way to prevent these negative consequences and improve overall health and longevity.
Smoking and Immune System
Smoking has a detrimental effect on the immune system, making individuals more susceptible to various diseases and health conditions. The harmful chemicals present in tobacco, such as nicotine and tar, weaken the immune system’s ability to fight off infections and diseases.
One of the major consequences of smoking on the immune system is an increased risk of heart disease and stroke. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the blood vessels, leading to the formation of plaque and narrowing of the arteries. This can result in heart attacks and strokes, which are major causes of death worldwide.
Furthermore, smoking is a leading cause of lung cancer and other respiratory diseases. The toxins in tobacco smoke can cause mutations in the DNA of lung cells, leading to the uncontrolled growth of cancer cells. Additionally, smoking damages the cilia in the lungs, which are responsible for clearing mucus and debris, making smokers more susceptible to respiratory infections.
In addition to its direct effects on the cardiovascular and respiratory systems, smoking also weakens the immune system’s ability to fight off infections and diseases. This can lead to an increased risk of various infections, such as pneumonia, bronchitis, and influenza. Smokers may also experience slower wound healing and increased susceptibility to skin infections.
It is important to note that smoking is not only harmful to the person who smokes, but also to those around them. Secondhand smoke can also weaken the immune system and increase the risk of respiratory infections, especially in children.
Overall, smoking has a detrimental effect on the immune system, increasing the risk of various diseases and compromising overall health. Quitting smoking can significantly improve the immune system’s function and reduce the risk of developing smoking-related illnesses.
Smoking and Vision Problems
Smoking is a harmful habit that can have serious consequences for your overall health. One area that is often overlooked is the impact smoking can have on your vision. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can cause a wide range of vision problems, including cataracts, macular degeneration, and dry eye syndrome.
Cataracts are a common vision problem that can be caused by smoking. Cataracts occur when the lens of the eye becomes cloudy, leading to blurry vision. Smoking increases the risk of developing cataracts, and the more cigarettes you smoke, the greater the risk. Quitting smoking can help reduce the risk of cataracts and improve overall eye health.
Macular degeneration is another vision problem that is linked to smoking. This condition affects the macula, the part of the eye responsible for central vision. Smoking can damage the blood vessels in the eyes, leading to the development of macular degeneration. This condition can cause a loss of central vision, making it difficult to read, drive, and perform other everyday tasks.
Dry eye syndrome is a common condition that can cause discomfort and vision problems. Smoking can worsen this condition by irritating the eyes and reducing tear production. Dry eye syndrome can cause symptoms such as redness, itching, and a gritty sensation in the eyes. Quitting smoking can help improve tear production and alleviate the symptoms of dry eye syndrome.
Overall, smoking is a dangerous habit that can have serious consequences for your vision. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can increase the risk of developing cataracts, macular degeneration, and dry eye syndrome. Quitting smoking is the best way to protect your vision and reduce the risk of these vision problems.
Smoking and Skin Health
Smoking has a detrimental effect on skin health, causing various skin problems and accelerating the aging process. The harmful chemicals in tobacco smoke, such as nicotine and carbon monoxide, reduce blood flow to the skin, leading to a lack of oxygen and nutrients. This can result in a dull complexion, uneven skin tone, and the appearance of wrinkles and fine lines.
Furthermore, smoking increases the risk of developing skin cancer. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the DNA in skin cells, leading to the formation of cancerous cells. This risk is particularly high for smokers who also spend a lot of time in the sun, as the combination of smoking and sun exposure further increases the likelihood of developing skin cancer.
Smoking also impairs wound healing and can lead to delayed recovery from skin injuries or surgeries. The reduced blood flow caused by smoking can hinder the delivery of necessary nutrients and oxygen to the wound site, slowing down the healing process. This can result in infections, scarring, and prolonged recovery time.
In addition to these skin-related issues, smoking is a major risk factor for various other health problems, including stroke, heart disease, and lung cancer. The addictive nature of nicotine makes quitting smoking a challenging task, but it is crucial for improving overall health and preserving skin health. Quitting smoking can lead to significant improvements in skin appearance and reduce the risk of skin cancer and other smoking-related diseases.
Quitting Smoking and Its Benefits
Quitting smoking has numerous benefits for both your physical and mental health. One of the most significant benefits is the improvement in lung function. Smoking damages the lungs and can lead to various respiratory problems such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema. When you quit smoking, your lung capacity starts to improve, allowing you to breathe more easily and reducing the risk of developing these diseases.
In addition to improving lung health, quitting smoking also greatly reduces the risk of heart disease. Smoking is a major risk factor for heart attacks and strokes. The chemicals in tobacco smoke can damage the lining of the arteries, leading to the development of atherosclerosis. By quitting smoking, you can lower your risk of heart disease and decrease the chances of experiencing a heart attack or stroke.
Another benefit of quitting smoking is the decreased risk of premature death. Smoking is responsible for numerous deaths every year, with diseases like lung cancer and heart disease being the leading causes. By quitting smoking, you can significantly reduce your risk of developing these deadly diseases and increase your chances of living a longer, healthier life.
Quitting smoking also helps to break the cycle of nicotine addiction. Nicotine is a highly addictive substance found in tobacco products, and quitting smoking can be a challenging process. However, once you break free from the addiction, you will experience a sense of freedom and control over your life. You will no longer be controlled by the need for nicotine and can focus on improving your overall well-being.
Overall, quitting smoking has numerous benefits for your health and well-being. It improves lung function, reduces the risk of heart disease and premature death, and helps break the cycle of nicotine addiction. If you are a smoker, consider quitting today to start enjoying these benefits and improve your quality of life.
Question-answer:
What are the harmful side effects of tobacco use?
Tobacco use has numerous harmful side effects, including an increased risk of lung cancer, heart disease, stroke, and other respiratory diseases. It can also lead to tooth decay, bad breath, and stained teeth. Additionally, tobacco use can cause addiction and can negatively impact one’s overall physical fitness and stamina.
How does tobacco use increase the risk of lung cancer?
Tobacco use, especially smoking cigarettes, is the leading cause of lung cancer. When tobacco is smoked, it releases harmful chemicals that are inhaled into the lungs. These chemicals can damage the cells in the lungs and lead to the development of cancer over time.
Can tobacco use cause other types of cancer?
Yes, tobacco use is also associated with an increased risk of developing various types of cancer, including cancers of the mouth, throat, esophagus, pancreas, bladder, kidney, and cervix. The harmful chemicals in tobacco can damage the DNA in cells, leading to the uncontrolled growth of cancer cells.
What are some other harmful effects of tobacco use?
In addition to the increased risk of cancer, tobacco use can also lead to heart disease and stroke. The chemicals in tobacco can damage the blood vessels, causing them to narrow and restrict blood flow. This can result in high blood pressure, heart attacks, and strokes. Tobacco use can also cause respiratory diseases such as chronic bronchitis and emphysema.